ASCOBANS
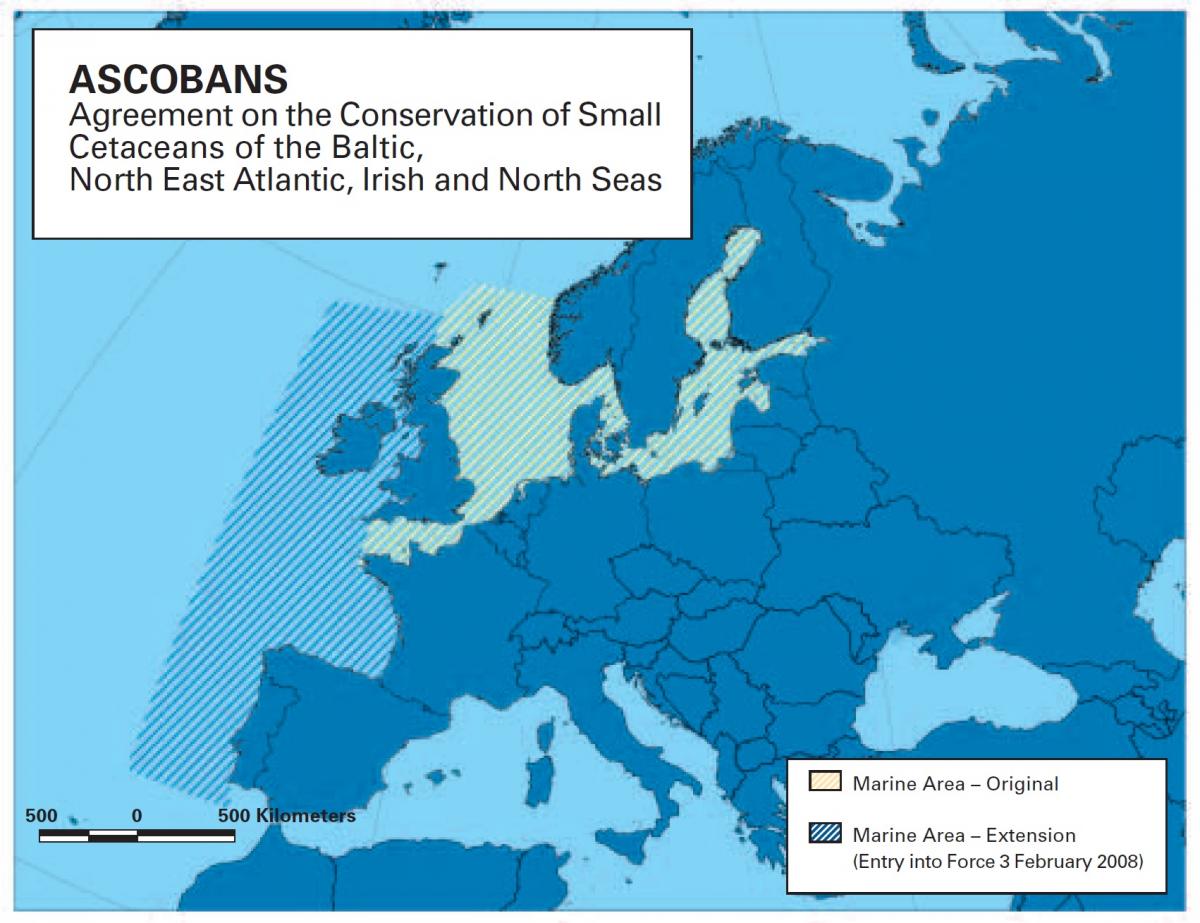
The Agreement was approved in Geneva in September 1991, during the Third Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS or Bonn Convention) pursuant to its Article IV (4). The Agreement was concluded in March 1992, opened for signature as the Agreement on the Conservation of Small Cetaceans of the Baltic and North Seas (ASCOBANS), and entered into force in 1994. In February 2008, an extension of the agreement area came into force which changed the name to "Agreement on the Conservation of Small Cetaceans of the Baltic, North East Atlantic, Irish and North Seas".
The Agreement Area is defined as follows:
"... the marine environment of the Baltic and North Seas and contiguous area of the North East Atlantic, as delimited by the shores of the Gulfs of Bothnia and Finland; to the south-east by latitude 36°N, where this line of latitude meets the line joining the lighthouses of Cape St. Vincent (Portugal) and Casablanca (Morocco); to the south-west by latitude 36°N and longitude 15°W; to the north-west by longitude 15° and a line drawn through the following points: latitude 59°N/longitude 15°W, latitude 60°N/longitude 05°W, latitude, 61°N/longitude 4W;latitude 62N/ longitude 3W; to the north by latitude 62°N; and including the Kattegat and the Sound and Belt passages."
The Secretary General of the United Nations has assumed the functions of Depository of the Agreement. ASCOBANS is open for accession by all Range States (i.e. any state that exercises jurisdiction over any part of the range of a species covered by the Agreement or whose flag vessels engage in operations adversely affecting small cetaceans in the Agreement area) and by regional economic integration organisations.
The treaty text can be accessed here.
ASCOBANS is administered by United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), and secretariat services are provided by CMS. The working language of the Secretariat is English.
Countries
| Title | Status | Status date | Party number | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | Party | 1993 | North Sea | |
| Denmark | Party | 1993 | Baltic Sea, North Sea | |
| Estonia | Non-Party Range State | Baltic Sea | ||
| European Union | Signed but not ratified | 1992 | ||
| Finland | Party | 1999 | Baltic Sea | |
| France | Party | 2005 | Atlantic Ocean, North Sea | |
| Germany | Party | 1993 | Baltic Sea, North Sea | |
| Ireland | Non-Party Range State | Atlantic Ocean | ||
| Latvia | Non-Party Range State | Baltic Sea | ||
| Lithuania | Party | 2005 | Baltic Sea | |
| Netherlands | Party | 1992 | North Sea | |
| Norway | Non-Party Range State | North Sea | ||
| Poland | Party | 1996 | Baltic Sea | |
| Portugal | Non-Party Range State | Atlantic Ocean | ||
| Russia | Non-Party Range State | Baltic Sea | ||
| Spain | Non-Party Range State | Atlantic Ocean | ||
| Sweden | Party | 1992 | Baltic Sea, North Sea | |
| United Kingdom | Party | 1993 | Atlantic Ocean, North Sea |



